Cardiac Rhythm Management
Restoring balance to your heart
One of the heart’s most important jobs is to beat at a consistent and regular pace in order to ensure that the body gets the right amount of blood flow. Sometimes the heart has trouble finding its rhythm, causing it to beat too fast or too slow for the body’s needs.
Our Cardiac Rhythm Management services provide comprehensive care for patients living with irregular heartbeat (or, arrhythmia) and other heart rhythm disorders. We offer advanced treatments, compassionate care, and the latest technologies to help restore your heart’s natural rhythm and improve your quality of life.
Understanding electrophysiology
While some arrhythmias can be fixed through electrophysiology, some patients will require more permanent treatments like an implantable pacemaker or minimally invasive procedure to keep their heart’s rhythm in check.
At Saint Agnes, we take a team approach to rhythm management, using the expertise of cardiologists, electrophysiologists, imaging specialists and cardiac surgeons to give you the highest quality, long-lasting results.
Electrophysiology services include
- 3-D Mapping with Biosense Webster Carto XP and St. Jude Medical ESI
- Diagnostic electrophysiology
- Electrophysiology studies and ablations
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) placement
- Permanent Pacemaker (PPM) placement
- Radiofrequency (RF) catheter ablation for arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation (Afib) and ventricular tachycardia (V-tach)
Advanced cardiac rhythm treatment options
If you're experiencing heart rhythm problems, you don’t have to face them alone. Our dedicated team is here to guide you on your journey to healing, providing support at every step. Click through the tiles below to learn more about the advanced treatment options available at Saint Agnes.

AVEIR™ DR Dual Chamber Leadless Pacemaker
Learn more
Maze Procedure for Atril Fibrillation
Learn more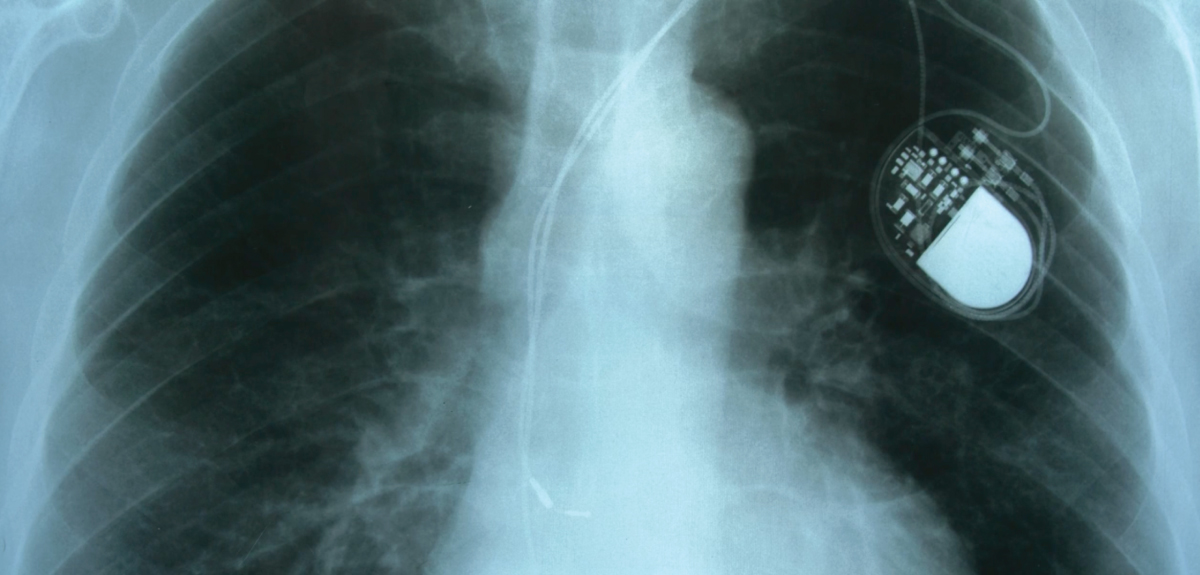
Pacemakers & Defibrillators
Learn more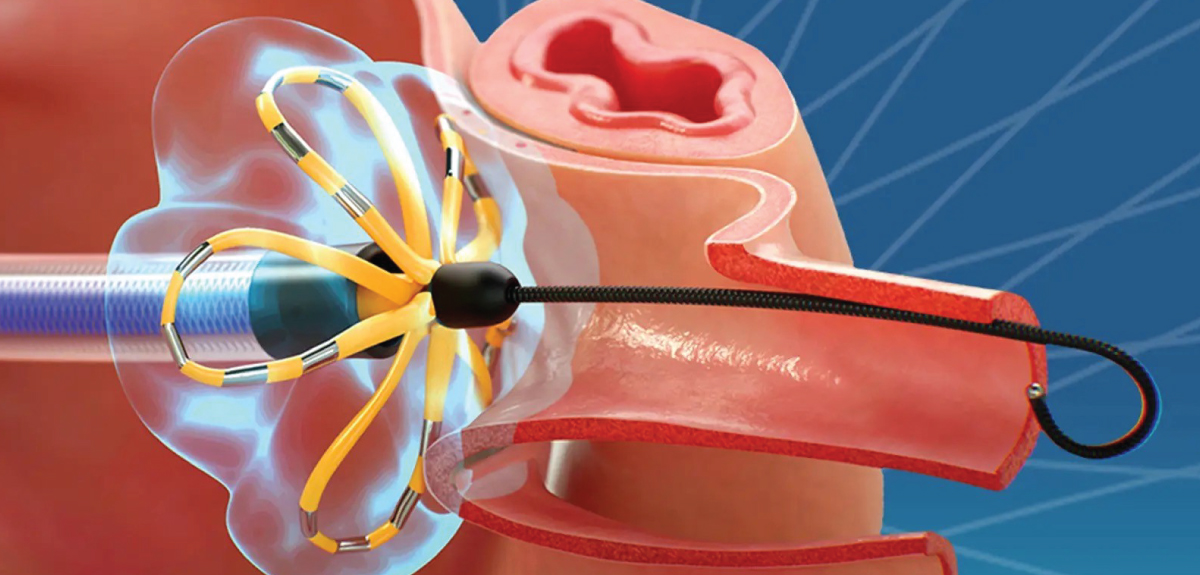
FARAPULSE™ Pulsed Field Ablation System
Learn more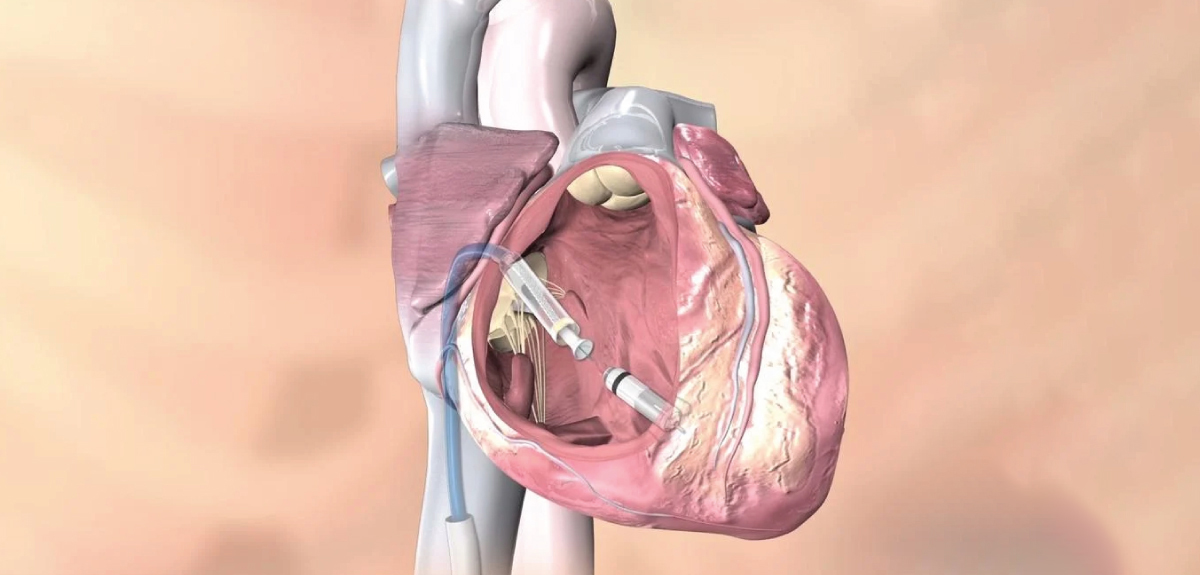
Micra® Leadless Pacemaker
Learn more