Heart Disease Prevention
Heart disease is the No. 1 killer of men and women, claiming a life every 33 seconds. Saint Agnes joins the American Heart Association to celebrate American Heart Month during the month of February and bring awareness to the dangers of heart disease and stroke all year long.
Understanding your risk of heart disease
Even if you're not personally at risk for heart disease, someone you love likely is. Factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, poor diet and lack of exercise can all increase your chances of developing heart disease. Genetics and family history can also play a role, making it even more important to stay informed.
Understanding your risk of heart disease is the first step toward a healthier future and many risk factors can be managed through lifestyle changes and preventive care. By knowing your personal risk and taking proactive steps, you can protect your heart and improve your overall well-being.
Click below to learn more about various risk factors that could increase your chance of developing heart disease and the treatment options available at Saint Agnes to help those in need of heart care.
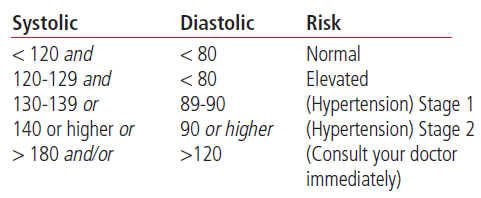
Blood pressure is something modifiable, but left untreated, it can cause what's called 'microvascular damage,' where over time, little rises in pressure put more and more strain on the cardiovascular system. That's why blood pressure is called the 'silent killer.
There's a lot of evidence that lifestyle modifications have a greater benefit in lowering blood pressure than medications if you're correctly following the recommendations of your doctor. With diet and exercise, it's not just about what you need to stop, but what you can start.
Think positively.
When your blood pressure is elevated, your heart is forced to work harder. If left untreated, high blood pressure can cause damage to the arteries and to your heart itself.

High cholesterol levels greatly increase a person’s risk of heart disease. When it comes to understanding cholesterol, it’s important to know your total, LDL and HDL cholesterol numbers. Don’t distress if you find your cholesterol to be on the high side. Talk to your physician to help get your cholesterol back on track. There are many options to bring your cholesterol back to a "healthy" level so talk to your physician to figure out what positive steps are both doable and agreeable for you.
LDL Cholesterol
LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein or "bad" cholesterol) contributes to plaque buildup and clogging of the arteries.
- Below 130 – Desirable
- 130-159 – Borderline
- Above 160 – High
HDL Cholesterol
HDL (High Density Lipoprotein or "good" cholesterol) protects the heart by helping to remove LDL deposits from your arteries.
- Above 60 – Desirable
- 50-59 – Borderline
- Below 50 – High
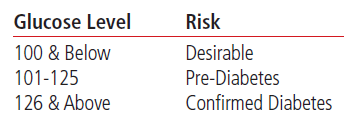
Diabetes significantly increases your risk of heart disease. It is an especially important risk factor for women because they are three times more likely to die of heart disease than men with diabetes.
Reduce your risk
If you have diabetes, it is important to get regular checkups and to work with your doctor to keep it in check through meal planning, exercise, weight loss and, if applicable, medication and self-monitoring.
Physical inactivity can lead to obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure – all of which greatly increase the risk of heart disease. The American Heart Association advises at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise a day, five times a week.
Always check with your doctor before starting a new exercise routine to determine what level of physical activity is right for you.
Smoking and vaping pose serious risks to your heart health. The chemicals in cigarettes and e-cigarettes can damage blood vessels, increase blood pressure, and raise the risk of dangerous buildup in your arteries, leading to heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
Nicotine, whether ingested from traditional cigarettes or vaping devices, strains the heart by increasing heart rate and blood pressure, making the heart work harder than it should. While some believe vaping is a "safer alternative," it still exposes the body to harmful toxins that can negatively impact cardiovascular health.
The best way to protect your heart is to quit smoking and vaping altogether — every step toward quitting lowers your risk and improves your overall well-being.
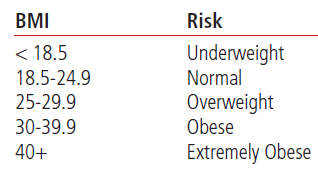
Excess weight puts significant strain on your heart and worsens several other heart disease risk factors, such as diabetes.
Know your Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI) is one method used to assess weight status and obesity. It allows you to compare your body weight, relative to your height, with the general population.
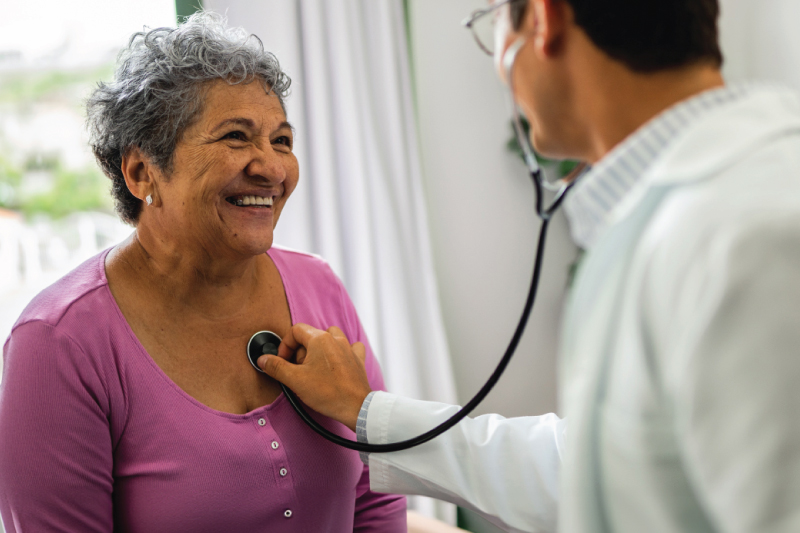

Advanced heart care close to home
We're proud to offer THREE NEW advanced treatment options for patients living with a leaky valve and irregular heart rhythm.
Learn more
Find a provider for your entire family
Looking for trusted, compassionate care for your whole family? Explore our list of care providers, dedicated to keeping you healthy at every stage of life.
Learn more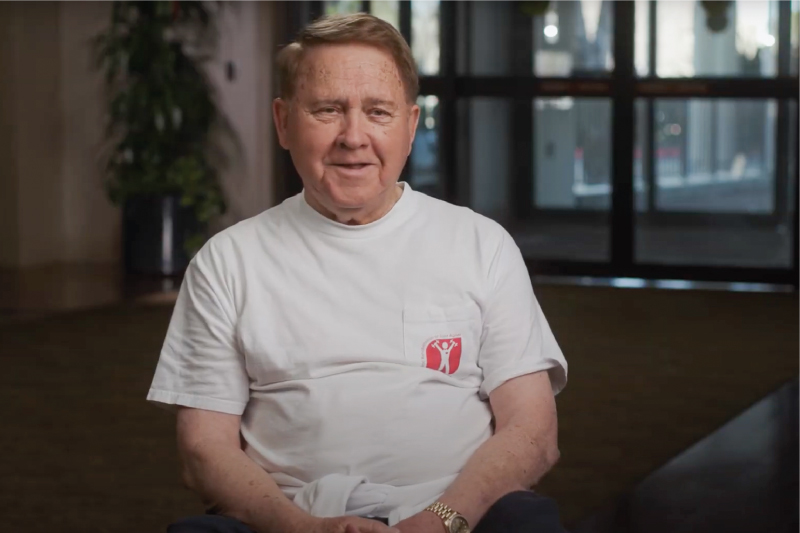
Less time recovering, more time living
MitraClip is a minimally-invasive heart procedure for mitral valve regurgitation, helping the heart pump more efficiently without open-heart surgery.
Watch Leo's story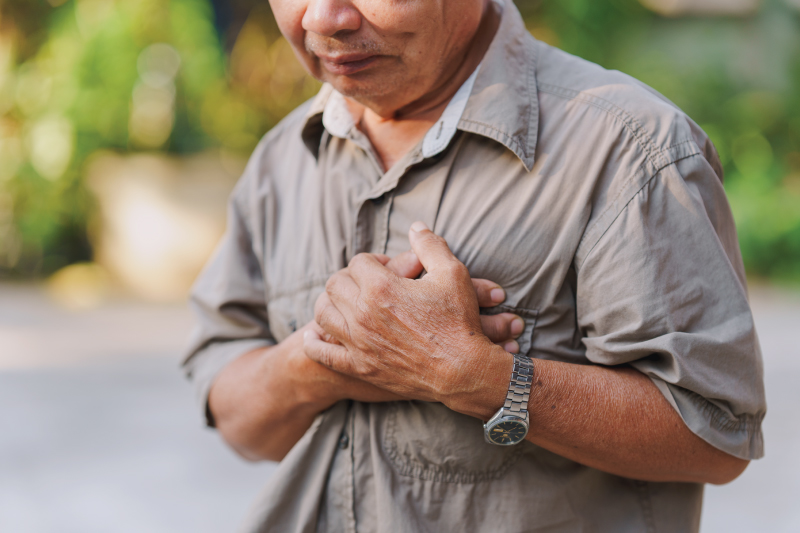
Warning signs of a heart attack
The warning signs of a heart attack look different in mena and women. Knowing the signs and symptoms can help you seek life-saving care quickly.
Know the signs